Healthy Retina
The benchmark for a healthy retina
Allergies
The abnormal response of sensitive eyes to contact with allergens and other irritating substances.
Dry Eye
Dry eye is a condition in which a person doesn't have enough quality tears to lubricate and nourish the eye. Tears are necessary for maintaining the health of the front surface of the eye and for providing clear vision. Dry eye is a common and often chronic problem, particularly in older adults.
Cataracts
A cataract is a cloudy or opaque area in the normally clear lens of the eye. Depending upon its size and location, it can interfere with normal vision. Most cataracts develop in people over age 55, but they occasionally occur in infants and young children. Usually cataracts develop in both eyes, but one may be worse than the other.
Floaters
Floaters are small, semitransparent or cloudy particles within the vitreous, which is the clear, jelly-like fluid that fills the inside of your eyes. These spots can appear as specks of various shapes and sizes, threadlike strands or cobwebs. Because they are in your eyes, they move as your eyes move and seem to dart away when you try to look at them directly. Though most floaters are harmless, they can be a sign of greater ocular health issues which can be diagnosed through your comprehensive eye exam.
glare/light sensitivity
Glare sensitivity is a debilitating loss of visual acuity in bright lighting, such as when near a bright light source or outdoors in bright sunlight. Patients suffering from glare sensitivity will be unable to see the separate contours of brightly lit objects, and their surroundings may merge into a “wall” of bright white. Glare sensitivity may be a symptom of certain eye conditions or could be a temporary side effect from some eye procedures and surgeries.
Glaucoma
Glaucoma is an eye disease in which the internal pressure in your eyes increases enough to damage your optic nerve and cause vision loss. The increased pressure occurs when the passages that allow fluid in your eyes to drain become clogged. The reasons the passages become blocked are not known.
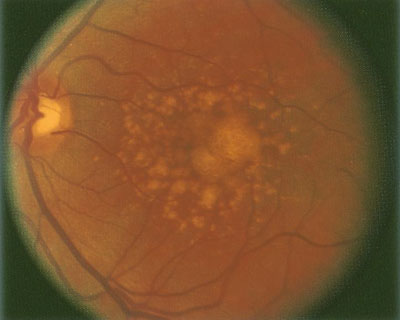
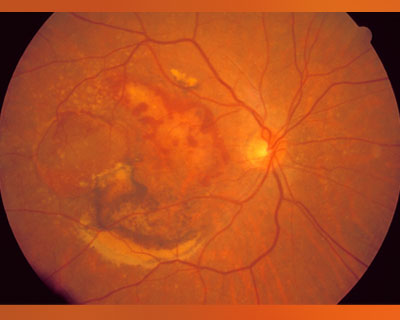
Macular Degeneration
Macular Degeneration occurs when there are changes to the macula, a small portion of the retina that is located on the inside back layer of the eye. AMD is a loss of central vision that can occur in two forms: "dry" (atrophic) and "wet" (exudative). In “dry” AMD parts of the macula get thinner with age and tiny clumps of protein called drusen (the yellowish spots in the image on the left) grow and obstruct vision. In “wet” AMD new, abnormal blood vessels grow under the retina. These vessels may leak blood or other fluids, causing scarring of the macula.